Definition:
Ultrasonic metal welding utilizes high – frequency vibration waves transmitted to the surface of the metals to be welded. Under pressure, the two metal surfaces rub against each other to form a fusion between molecular layers.
Principle:
Ultrasonic metal welding is a special method that uses the mechanical vibration energy of ultrasonic frequency to join the same or different metals. When metal is ultrasonically welded, no electric current is transmitted to the workpiece, nor is a high – temperature heat source applied to the workpiece. Only under static pressure, mechanical energy is converted into internal energy, deformation energy, and a limited temperature rise. Solid – phase welding occurs when the two base materials reach the recrystallization temperature.
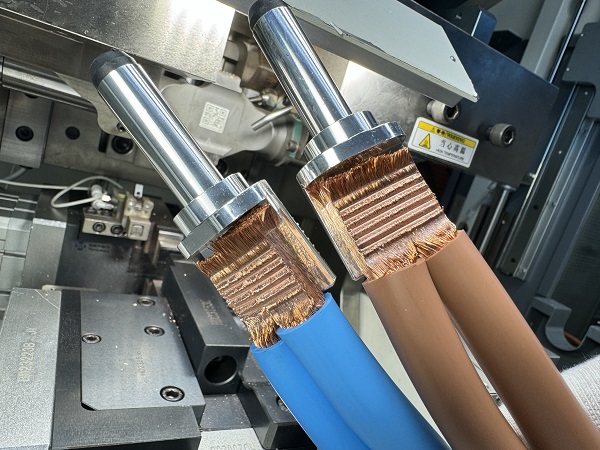
During the ultrasonic welding process, the transducer converts high – frequency electrical signals into ultrasonic vibration signals. The high – frequency vibrations are transmitted to the surface of the metal to be welded through the welding tool head. The oxide film on the interface metal is broken under the combined action of a certain pressure and the intense friction of ultrasonic vibration. The clean metal at the interface comes into contact, and under the combined effects of friction and ultrasonic softening, further plastic flow and diffusion occur, gradually increasing the connection area until a reliable connection is finally formed.

During the ultrasonic welding process, the transducer converts high – frequency electrical signals into ultrasonic vibration signals. The high – frequency vibrations are transmitted to the surface of the metal to be welded through the welding tool head. The oxide film on the interface metal is broken under the combined action of a certain pressure and the intense friction of ultrasonic vibration. The clean metal at the interface comes into contact, and under the combined effects of friction and ultrasonic softening, further plastic flow and diffusion occur, gradually increasing the connection area until a reliable connection is finally formed.

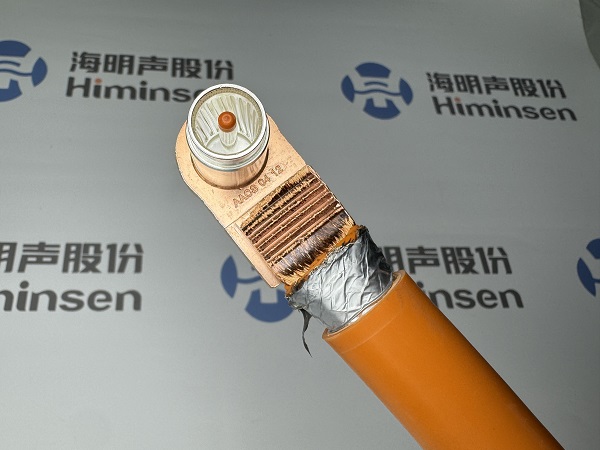
Ultrasonic metal welding utilizes the transmission of high – frequency vibration waves to the surfaces of two metals to be welded. Under pressure, the two metal surfaces rub against each other to form a fusion between molecular layers. This welding method does not transmit electric current or a high – temperature heat source to the workpiece. Instead, under static pressure, mechanical energy is converted into internal energy, deformation energy, and a limited temperature rise, thereby achieving solid – phase welding.
The working process of ultrasonic metal welding can be divided into the following steps:
Conversion of mechanical energy into internal energy and deformation energy: The ultrasonic generator converts electrical energy into mechanical vibration energy, which is transmitted to the welding head through the transducer and the horn. The welding head transfers the vibration energy to the surfaces of the metals to be welded, causing them to rub against each other and generate heat and deformation.
Metallurgical bonding between joints: Under static pressure, the molecular layers between the two metal surfaces fuse together to form a metallurgical bond. This bonding method does not require the melting of the metal but instead undergoes a recrystallization process at a temperature below the melting point.
Overcoming spatter and oxidation phenomena: Since no spatter and oxidation occur during the ultrasonic welding process, it can effectively connect the same or different metals. This method is suitable for welding fine wires or thin – sheet materials of non – ferrous metals such as copper, silver, aluminum, and nickel.











0条评论